Climate Action Planning (courtesy BBC)

20/11/2021
Developing a 1.5°C-compatible climate action plan is a vital step for cities to respond to the climate crisis. It enables cities to identify, and form an equitable strategy to address, their biggest sources of emissions and their climate risks. The next few years are critical, and cities need to act now – keeping global temperatures within safe levels requires most cities to peak their emissions by 2020, and halve them by 2030, on route to climate neutrality. The good news is that cities now have access to a wealth of knowledge, tools and other resources to help them do this, as well as the insights and experience of cities which have already published, and are implementing, 1.5°C climate action plans.
A deal aimed at staving off dangerous climate change has been struck at the COP26 summit in Glasgow.
Main achievements of the deal:
- Re-visiting emissions-cutting plans next year to try to keep 1.5°C target reachable
- The first ever inclusion of a commitment to limit coal use
- Increased financial help for developing countries
The Glasgow Climate Pact is the first ever climate deal to explicitly plan to reduce coal, the worst fossil fuel for greenhouse gases.
The deal also presses for more urgent emission cuts and promises more money for developing countries - to help them adapt to climate impacts.
But the pledges don't go far enough to limit temperature rise to 1.5°C.
A commitment to phase out coal that was included in earlier negotiation drafts led to a dramatic finish after India led opposition to it.
India's climate minister Bhupender Yadav asked how developing countries could promise to phase out coal and fossil fuel subsidies when they "have still to deal with their development agendas and poverty eradication".
In the end, countries agreed to "phase down" rather than "phase out" coal, amid expressions of disappointment by some. COP26 President Alok Sharma said he was "deeply sorry" for how events had unfolded.
Evasive words, but deal shows progress
He fought back tears as he told delegates that it was vital to protect the agreement as a whole.
The UK's Prime Minister Boris Johnson said he hoped the world would "look back on COP26 in Glasgow as the beginning of the end of climate change", promising to "continue to work tirelessly towards that goal". He added:
There is still a huge amount more to do in the coming years. But today's agreement is a big step forward and, critically, we have the first ever international agreement to phase down coal and a roadmap to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees.
US climate envoy John Kerry said:
We are in fact closer than we have ever been before to avoiding climate chaos and securing cleaner air, safer water and a healthier planet.
How the final day unfolded
But UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres sounded a less enthusiastic note, saying:
Our fragile planet is hanging by a thread. We are still knocking on the door of climate catastrophe. It is time to go into emergency mode - or our chance of reaching net zero will itself be zero.
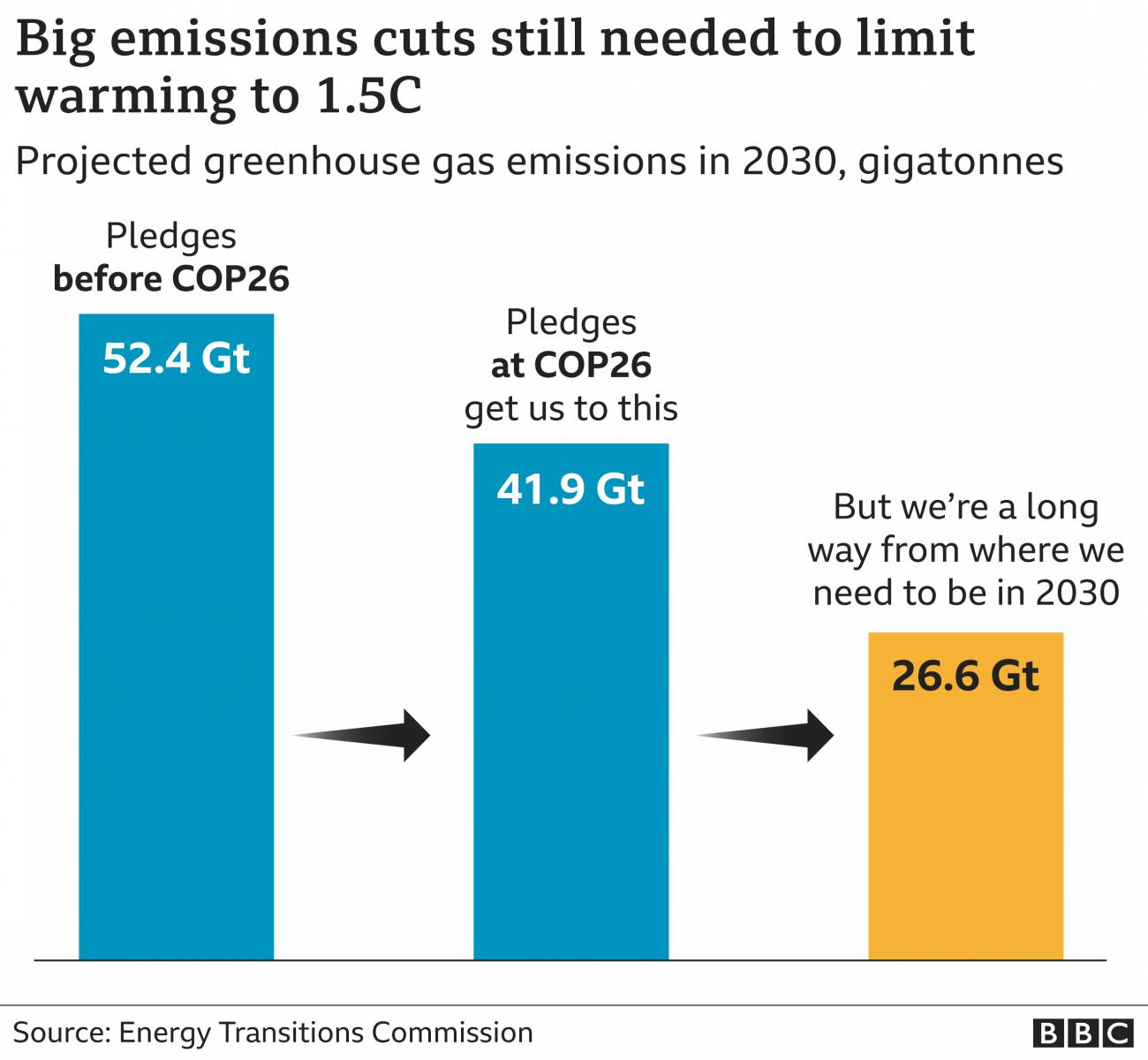
As part of the agreement, countries have pledged to meet next year to pledge further major carbon cuts so that the goal of 1.5°C can be reached. Current pledges, if fulfilled, are only though to limit global warming to 2.4°C.
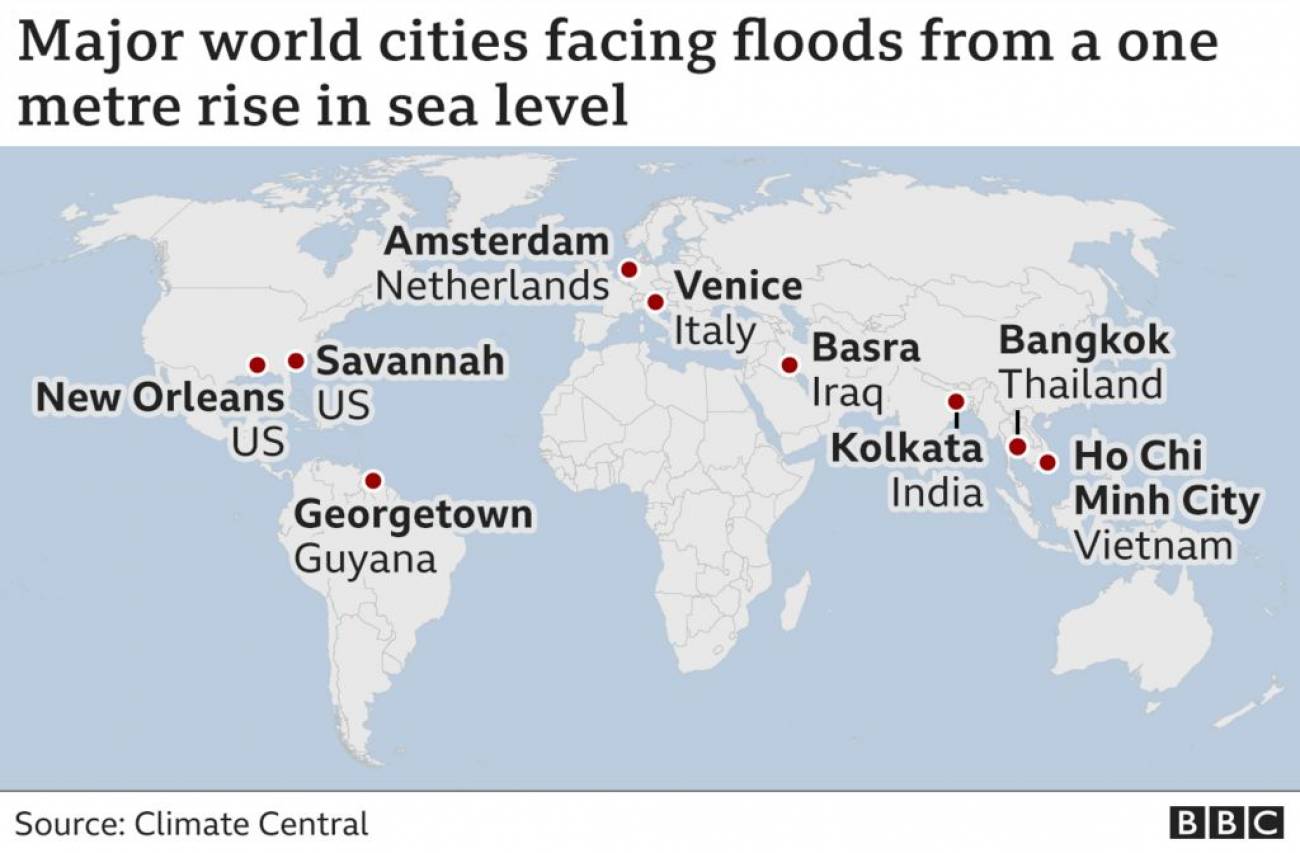
If global temperatures rise by more than 1.5°C, scientists say the Earth is likely to experience severe effects such as million more people will be exposed to extreme heat.


Source: How Heidelberg built one of the world’s largest carbon-neutral districts
Swiss environment minister Simonetta Sommaruga said:
We would like to express our profound disappointment that the language we agreed on, on coal and fossil fuels subsidies has been further watered down as a result of an untransparent process.
Despite the weakening of language around coal, some observers will still see the final deal as a victory, underlining that it is the first-time coal is explicitly mentioned in UN documents of this type.
Coal is responsible for about 40% of CO2 emissions each year, making it central in efforts to keep within the 1.5°C target. To meet this goal, agreed in Paris in 2015, global emissions need to be reduced by 45% by 2030 and to nearly zero by mid-century.
They changed a word but they can't change the signal coming out of this COP, that the era of coal is ending,
said Greenpeace international executive director Jennifer Morgan.
It's in the interests of all countries, including those who still burn coal, to transition to clean renewable energy.
However, Lars Koch, a policy director for charity ActionAid, said it was disappointing that only coal was mentioned.
This gives a free pass to the rich countries who have been extracting and polluting for over a century to continue producing oil and gas,
he said.
Sara Shaw, from Friends of the Earth International, said the outcome was "nothing less than a scandal". She added:
Just saying the words 1.5 degrees is meaningless if there is nothing in the agreement to deliver it. COP26 will be remembered as a betrayal of global South countries.
Finance was a contentious issue during the conference. A pledge by developed nations to provide $100bn per year to emerging economies, made in 2009, was supposed to have been delivered by 2020. However, the date was missed.
It's designed to help developing nations adapt to climate effects and make the transition to clean energy. In an effort to mollify delegates, Mr. Sharma said around $500bn would be mobilised by 2025.
Scientists say extreme weather events, such as severe flooding, are becoming more frequent because of climate change
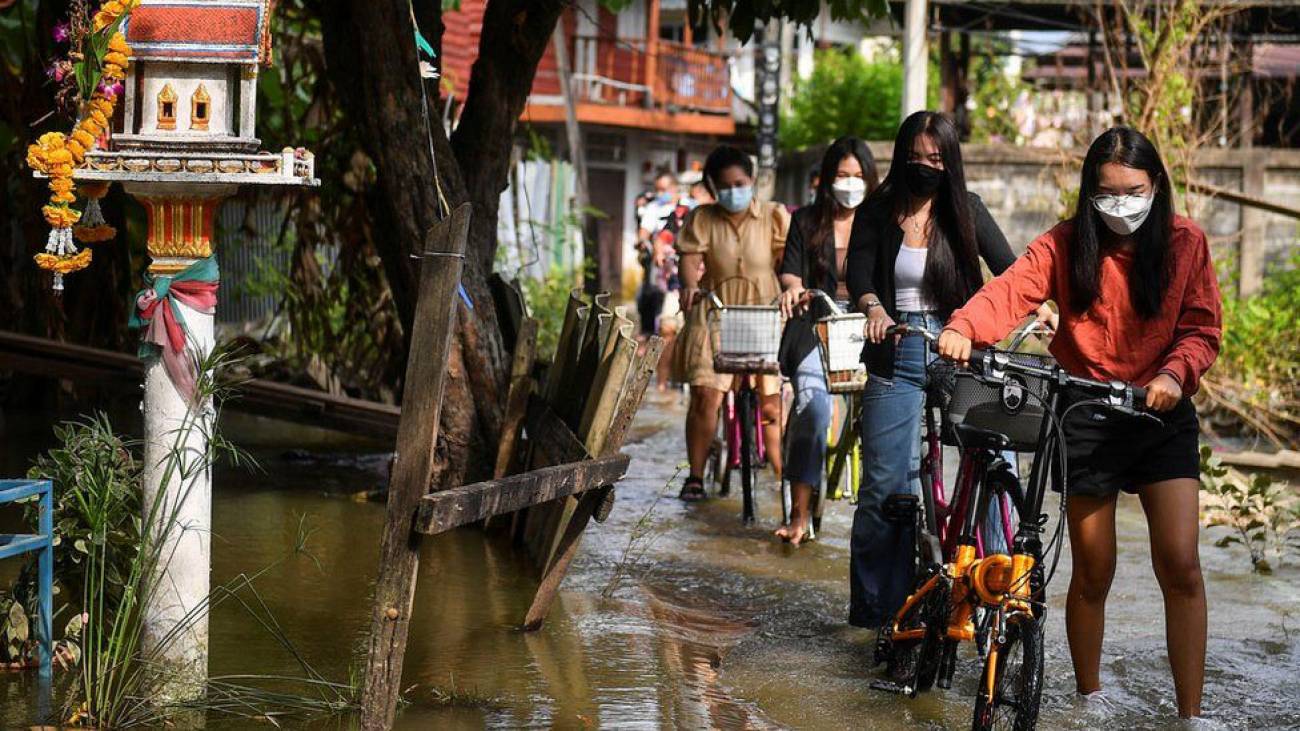

Source: REUTERS
But poorer countries had been calling throughout the meeting for funding through the principle of loss and damage - the idea that richer countries should compensate poorer ones for climate change effects they can't adapt to.
This was one of the big disappointments of the conference for many delegations. Despite their dissatisfaction, several countries that stood to benefit backed the agreement on the basis that talks on loss and damage would continue.
Delegations pushing for greater progress on the issue included those from countries in Africa, such as Guinea and Kenya, as well as Latin American states, small island territories and nations in Asia such as Bhutan.
Lia Nicholson, delegate for Antigua and Barbuda, and speaking on behalf of small island states, said:
We recognise the presidency's efforts to try and create a space to find common ground. The final landing zone, however, is not even close to capturing what we had hoped.









